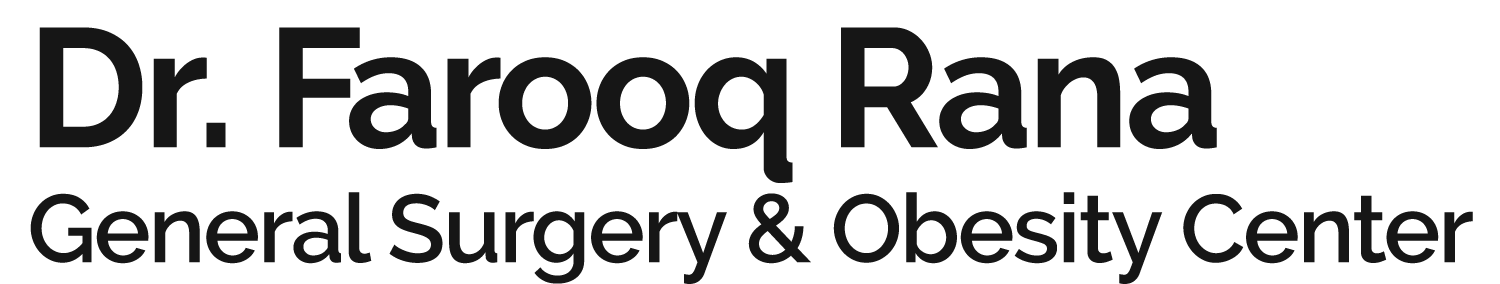Non-Surgical Approach
Adjustment Diets:
To controle the weight, patients need to reduce the caloric intake to a level lower than the caloric consumption. This asks for foodadjustements without causing food shortage. Less calories does not always mean less quantities of food. The composition of the food is the most important thing. That is why patïents need to see a dietician.
Physical Exercise:
Also the consumption of calories is very important. This can be stimulated by physical excercises. An excercise from minimum 30 minutes a day (on top of your daily activities) and a moderate intensity. For example walking, swimming, running…
Medication:
The medication Orlistat (Alli/Xenical) reduces the absorption of fat. A study shows that Orlistat results in a very little weightloss.
Surgical Approach
Many studies show that a surgical intervention offers the highest chance of a succesful approach for each patient with morbid obesity.
- Significant weightloss
- Reducement of diseases (comorbidities) or complaints
- Increasement of the quality of life
There are 4 kinds of surgeries:
- Restrictive interventions where the stomach is reduced
- Malabsorptive interventions where the goal of the operation is focused on the malabsorption of nutrients
- Combination restrictive and malabsorptive interventions: reducing the stomach + reducing the absorption of fat and sugar
- Redo operation after bariatric surgery