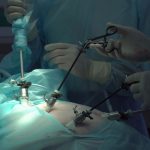
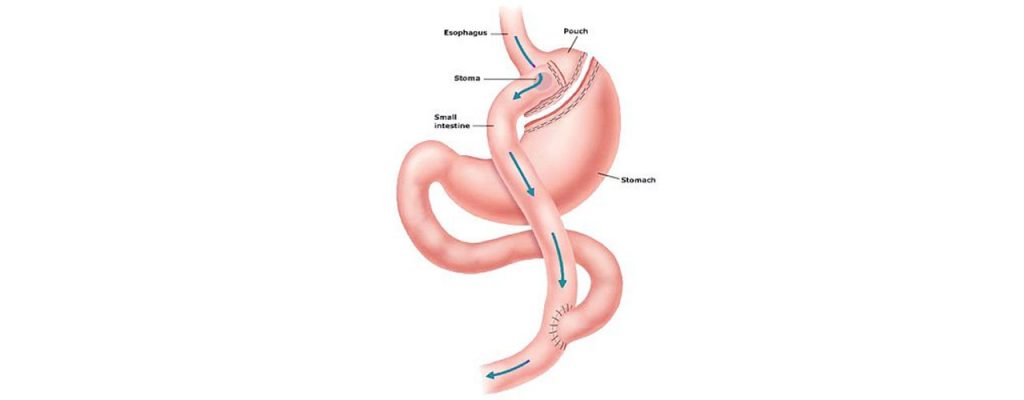
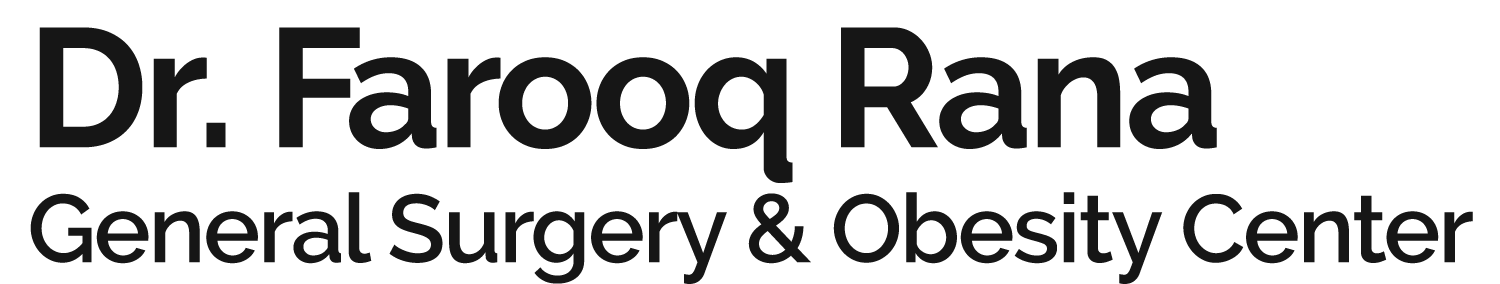It is a surgical procedure in which the stomach is divided into a small upper pouch and a larger lower “remnant” pouch. The small intestine is then rearranged to achieve malabsorption (Roux-en-Y bypass). Weight loss of 80% to 90% of excess body weight is typical of most large series of gastric bypass operations reported. The medically more significant effects include a dramatic reduction in comorbid conditions
Pros
- More weight loss than gastric banding.
- Type 2 diabetes is reversed in up to 90% of patients usually leading to a normal blood-sugar level without medication, sometimes within days of surgery. Furthermore, Type 2 diabetes is prevented by more than 30-fold in patients with pre-diabetes.
- Venous thromboembolic disease signs such as leg swelling are typically alleviated.
- A study in a large comparative series of patients showed an 89% reduction in mortality over the five years following surgery, compared to a non-surgically treated group of patients.
Cons
- Difficult to reverse.
- Higher chance of vitamin shortage than gastric band or gastric sleeve.
- Higher chance of surgery-related problems than gastric band.
Adapted from: Bariatric surgery procedures. American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) website. asmbs.org/patients/bariatric-surgery-procedures. Accessed May 24, 2016.