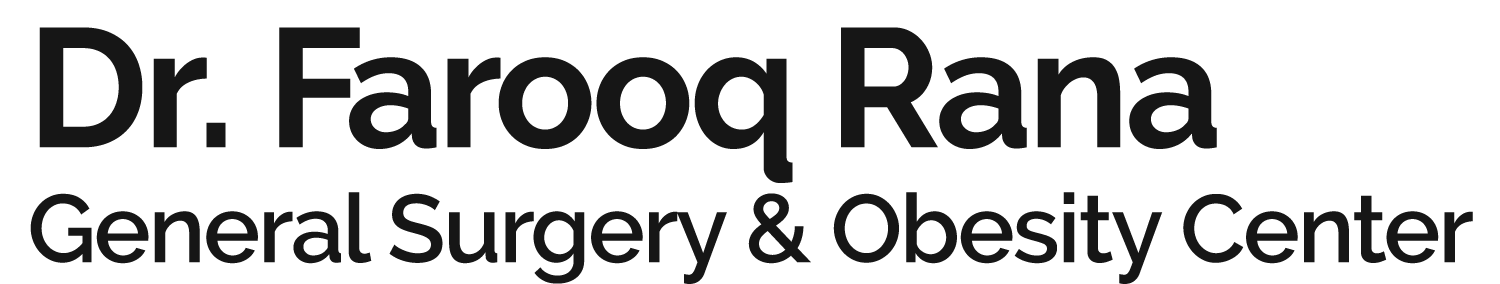Overview
Hernia is one of the most common surgical problem encountered in all age groups. Hernia may be without any symptoms but in majority it causes discomfort and affect routine activities of life. Especially on exercise and heavy work hernia becomes large and painful. Hernia needs to be repaired in all age groups and there is no medical treatment available for the treatment of hernia. Undue delay in the treatment of hernia can result in serious complications. So, any swelling on the abdomen that comes and goes and sometimes disappear on lying down can be a hernia and needs consultation from a General Surgeon for confirmation and management.
Symptoms
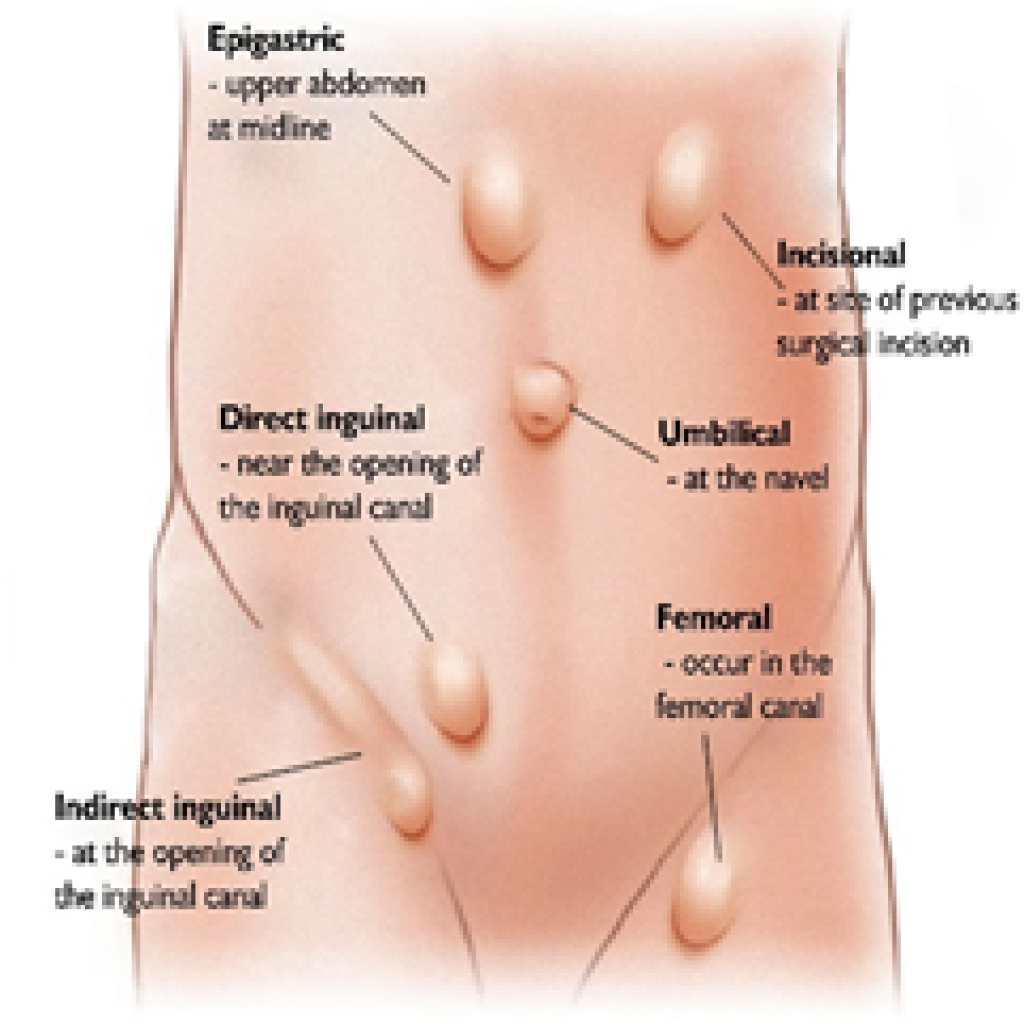
- A hernia present with a swelling which becomes more obvious when you’re upright, especially if you cough or strain.
- Pain or discomfort, especially when bending over, coughing or lifting
- A heavy or dragging sensation
- In male groin hernia may be associated with urinary symptoms and testicular pain.
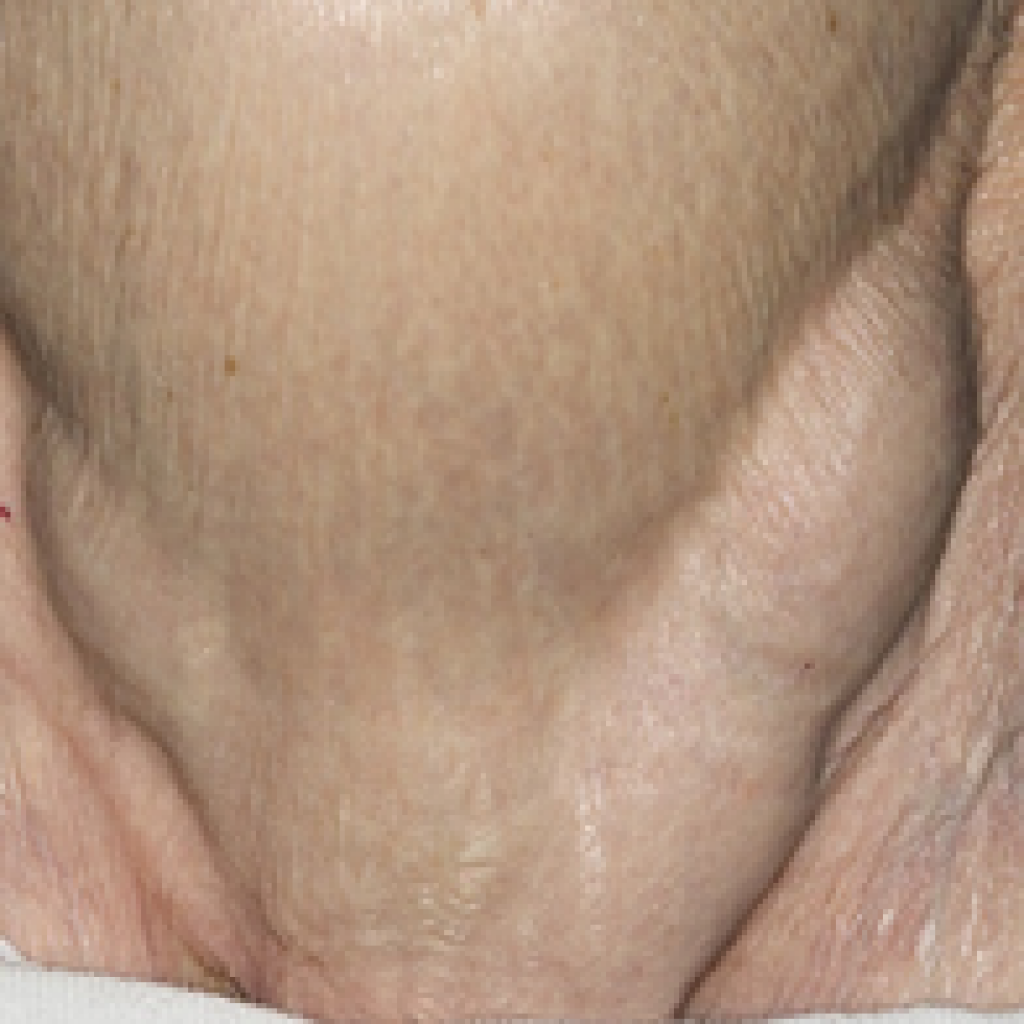
Types of Hernia
Hernias can commonly be found in following areas:
Groin: An inguinal hernia is common type of hernia in men. It is a bulge in the groin that may reach the scrotum. Femoral hernia creates a bulge just below the groin. This is more common in Women.
Belly Button: A bulge in this region is produced by an umbilical or para-umbilical hernia.
Incisional Hernia: Past abdominal surgery can lead to an incisional hernia through the weak scar.
Recurrent Hernia: a hernia at the site of previous hernia repair is called recurrent hernia, needs careful evaluation to figure out the cause of recurrence.
Upper part of the stomach: a hiatal or hiatus hernia is caused by the upper part of the stomach pushing out of the abdominal cavity and into the chest cavity through an opening in the diaphragm.
Risk Factors
The risk factors with high likelihood for the development of a hernia include:
- Congenital because of the birth defects
- First degree relative with a hernia
- Male gender (groin hernia more common in men)
- Week tissue collagen disorder
- In elderly urinary obstruction because of enlarged prostate
- Chronic cough, such as from smoking.
- Chronic constipation.
Diagnosis:
A physical exam is usually all that’s needed to diagnose a hernia. Because standing and coughing can make a hernia more prominent, you’ll likely be asked to stand and cough or strain. If the diagnosis isn’t readily apparent, your doctor might order an imaging test, such as an abdominal ultrasound, CT scan or MRI.
Treatment:
Hernia can be repaired with conventional open surgery or by Laparoscopic keyhole surgery. Hernia operation can be performed with full anesthesia or spinal anesthesia that make your lower half of the body numb. Most of hernia are repaired using synthetic mesh with very good results.
Abdominal wall hernia can be repaired with modern laparoscopic surgery (keyhole surgery) with advantage of less pain and early return to work. Talk to your surgeon to discuss your options.